Category: Tools
All topics
-

OpenAI may have rehired Sam Altman, but AI needs more accountability, not ‘geniuses’
– in ToolsThe OpenAI employees had faith in Altman. They believed in his vision and they did…
-

Information Architecture meets the Philosophy of Information
Advancing the practical and theoretical basis for how we conceptualise and shape the infosphere.
-

Using Wikipedia as PR is a problem, but our lack of a critical eye is worse
That Wikipedia is used for less-than scrupulously neutral purposes shouldn’t surprise us – our lack…
-

Current alternatives won’t light up Britain’s broadband blackspots
Satellites, microwaves, radio towers – how many more options must be tried before the government…
-
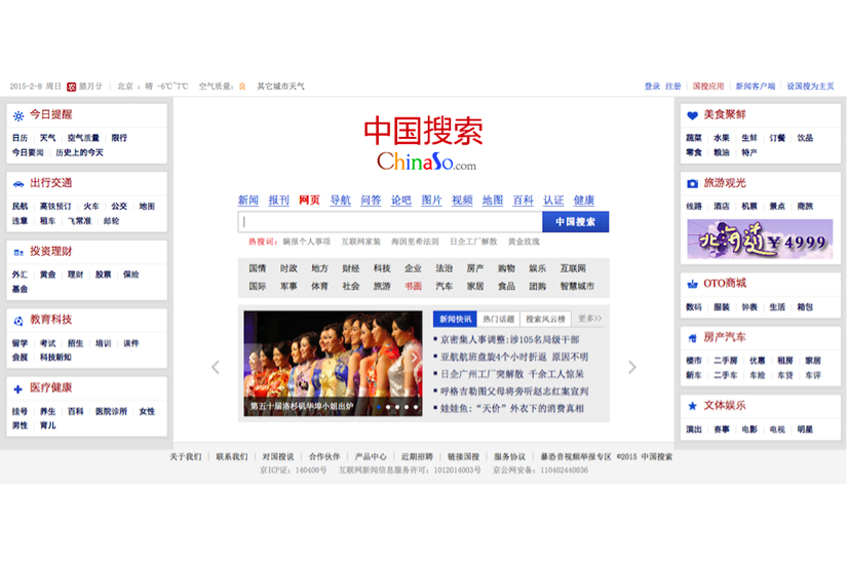
Will China’s new national search engine, ChinaSo, fare better than “The Little Search Engine that Couldn’t”?
Branded explicitly as “China Search: Authoritative National Search,” ChinaSo reinforces a sense of national identity.…
-

The social economies of networked cultural production (or, how to make a movie with complete strangers)
Looking at “networked cultural production”—ie the creation of cultural goods like films through crowdsourcing platforms—specifically…
-

Online crowd-sourcing of scientific data could document the worldwide loss of glaciers to climate change
The platform aims to create long-lasting scientific value with minimal technical entry barriers—it is valuable…


