Tag: gig work
All topics
-
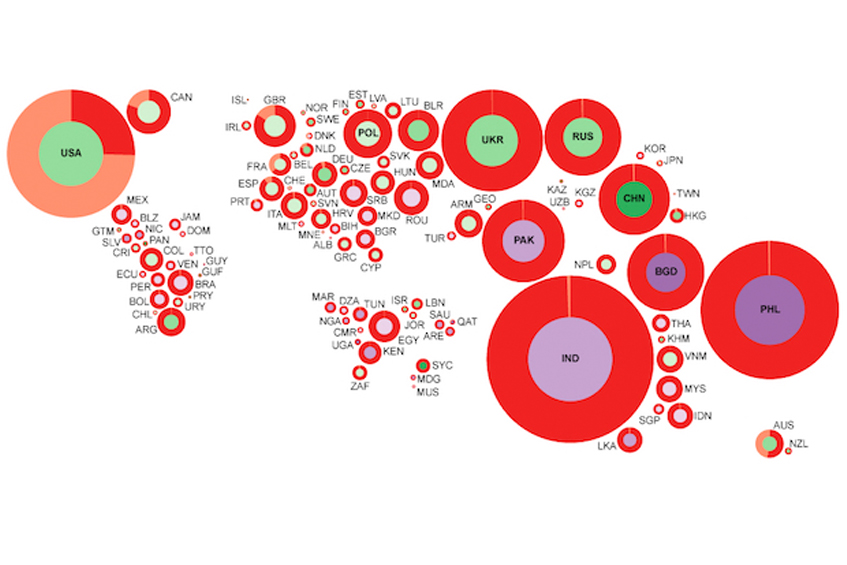
New Report: Risks and Rewards of Online Gig Work at the Global Margins
– in DevelopmentThe report poses questions for all stakeholders regarding how to improve the conditions and livelihoods…
-
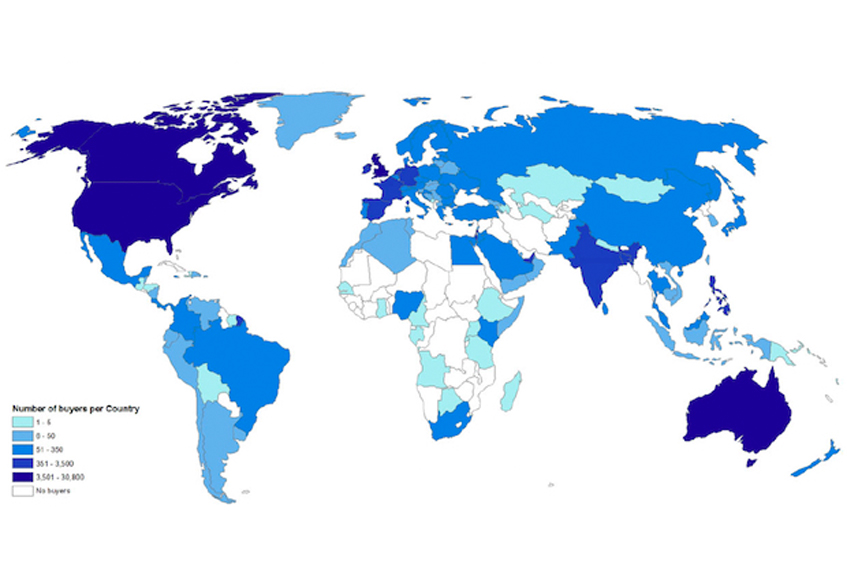
What Impact is the Gig Economy Having on Development and Worker Livelihoods?
– in DevelopmentReflecting on some of the key benefits and costs associated with these new digital regimes…
