Tag: darknet
All topics
-
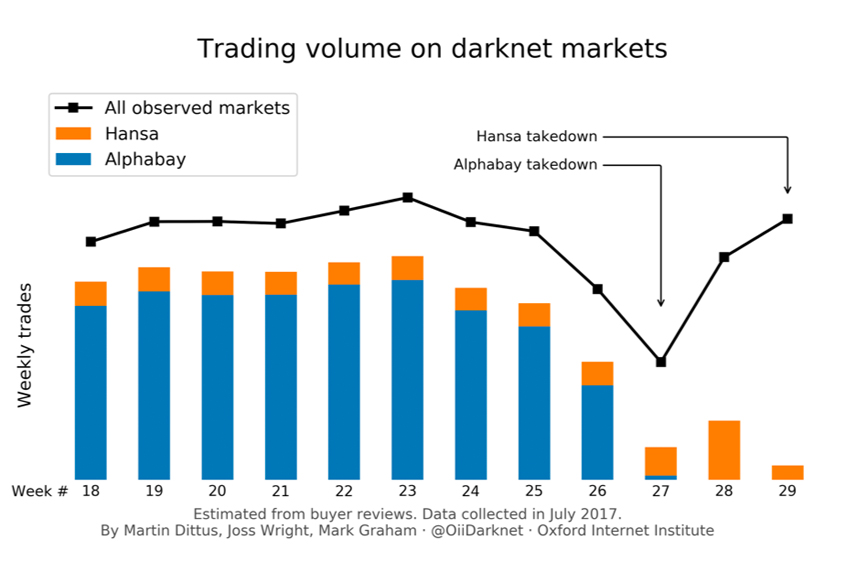
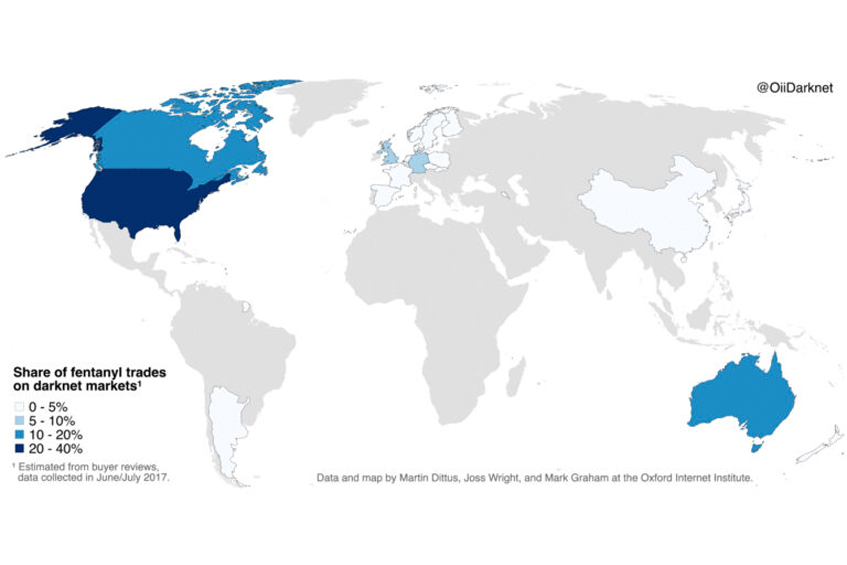
A distributed resilience among darknet markets?
– in EconomicsThe actions by law enforcement were deliberately structured to seed distrust in illicit trading platforms.…
-

Introducing Martin Dittus, Data Scientist and Darknet Researcher
Martin Dittus is a Data Scientist at the Oxford Internet Institute. The stringent ethics process…
-

Exploring the Darknet in Five Easy Questions
– in EconomicsWe caught up with Martin Dittus to find out some basics about darknet markets, and…