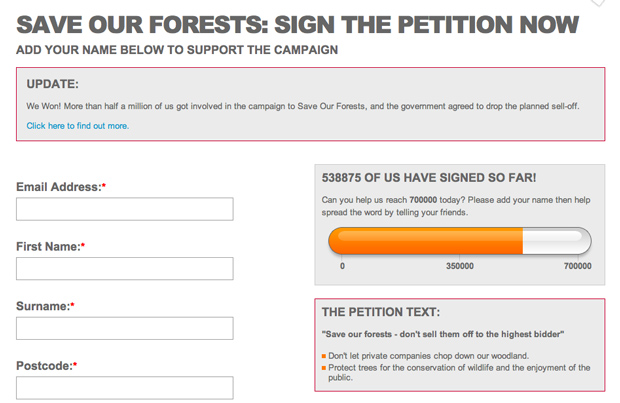
Category: Collective Action
All topics
-

Can e-participation be improved? Lessons from two successful initiatives.
Many initiatives have been launched, but some of them fail and/or are abandoned, contributing to…
-

Is crowdfunding at risk of being weaponized for extremist causes?
How do crowdfunding sites maintain their legitimacy as ‘open’ platforms while avoiding complicity with divisive,…
-

How useful are volunteer crisis-mappers in a humanitarian crisis?
Concerns have been raised about the quality of amateur mapping and data efforts, and the…
-

Controlling the crowd? Government and citizen interaction on emergency-response platforms
Government involvement in crowdsourcing efforts can actually be used to control and regulate volunteers from…
-

Do Finland’s digitally crowdsourced laws show a way to resolve democracy’s “legitimacy crisis”?
Discussing the digitally crowdsourced law for same-sex marriage that was passed in Finland and analysing…
-

Political polarisation on social media: do birds of a feather flock together on Twitter?
Twitter’s connections tend to be less about strong social relationships and more about connecting with…
-

Presenting the moral imperative: effective storytelling strategies by online campaigning organisations
Existing civil society focused organisations are also being challenged to fundamentally change their approach, to…
-

The global fight over copyright control: Is David beating Goliath at his own game?
We stress the importance of digital environments for providing contenders of copyright reform with a…