All Articles
All topics
-

Five reasons ‘technological solutions’ are a distraction from the Irish border problem
Discussing the focus on ‘technological solutions’ in the context of the Irish border debate.
-

Can “We the People” really help draft a national constitution? (sort of..)
There is a clear trend of greater public participation in the process of constitution making,…
-

Call for Papers: Government, Industry, Civil Society Responses to Online Extremism
Mapping and evaluating emerging public-private partnerships, technologies, and responses to online extremism.
-
How can we encourage participation in online political deliberation?
The Internet seems to provide an obvious opportunity to strengthen intra-party democracy and mobilise passive…
-

Making crowdsourcing work as a space for democratic deliberation
Is crowdsourcing conducive to deliberation among citizens or is it essentially just a consulting mechanism…
-

Habermas by design: designing public deliberation into online platforms
What particular platform features should we look to, to promote deliberative debate online?
-

Human Rights and Internet Technology: Six Considerations
– in EthicsThe United Nations Human Rights Council has reaffirmed many times that “the same rights that…
-

Could Counterfactuals Explain Algorithmic Decisions Without Opening the Black Box?
– in EthicsExploring the role of algorithms in our everyday lives, and how a “right to explanation”…
-
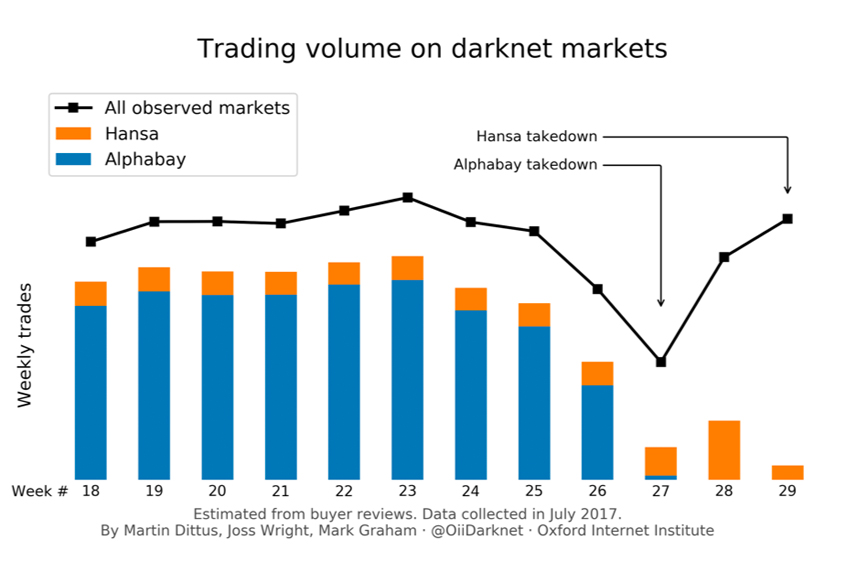
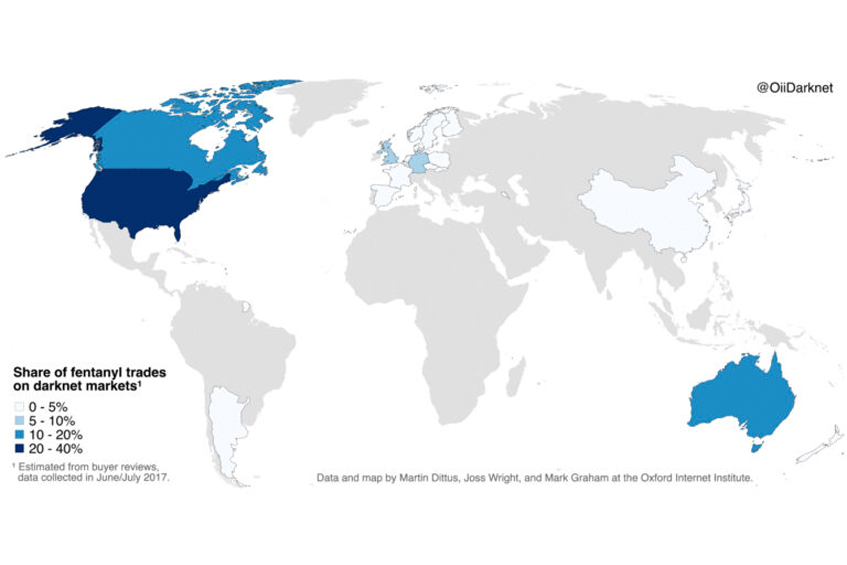
A distributed resilience among darknet markets?
– in EconomicsThe actions by law enforcement were deliberately structured to seed distrust in illicit trading platforms.…