‘Congratulations to my friend @Messina2012 on his role in the resounding Conservative victory in Britain’ tweeted David Axelrod, campaign advisor to Miliband, to his former colleague Jim Messina, Cameron’s strategy adviser, on May 8th. The former was Obama’s communications director and the latter campaign manager of Obama’s 2012 campaign. Along with other consultants and advisors and large-scale data management platforms from Obama’s hugely successful digital campaigns, Conservative and Labour used an arsenal of social media and digital tools to interact with voters throughout, as did all the parties competing for seats in the 2015 election.
The parties ran very different kinds of digital campaigns. The Conservatives used advanced data science techniques borrowed from the US campaigns to understand how their policy announcements were being received and to target groups of individuals. They spent ten times as much as Labour on Facebook, using ads targeted at Facebook users according to their activities on the platform, geo-location and demographics. This was a top down strategy that involved working out was happening on social media and responding with targeted advertising, particularly for marginal seats. It was supplemented by the mainstream media, such as the Telegraph for example, which contacted its database of readers and subscribers to services such as Telegraph Money, urging them to vote Conservative. As Andrew Cooper tweeted after the election, ‘Big data, micro-targeting and social media campaigns just thrashed “5 million conversations” and “community organising”’.
He has a point. Labour took a different approach to social media. Widely acknowledged to have the most boots on the real ground, knocking on doors, they took a similar ‘ground war’ approach to social media in local campaigns. Our own analysis at the Oxford Internet Institute shows that of the 450K tweets sent by candidates of the six largest parties in the month leading up to the general election, Labour party candidates sent over 120,000 while the Conservatives sent only 80,000, no more than the Greens and not much more than UKIP. But the greater number of Labour tweets were no more productive in terms of impact (measured in terms of mentions generated: and indeed the final result).
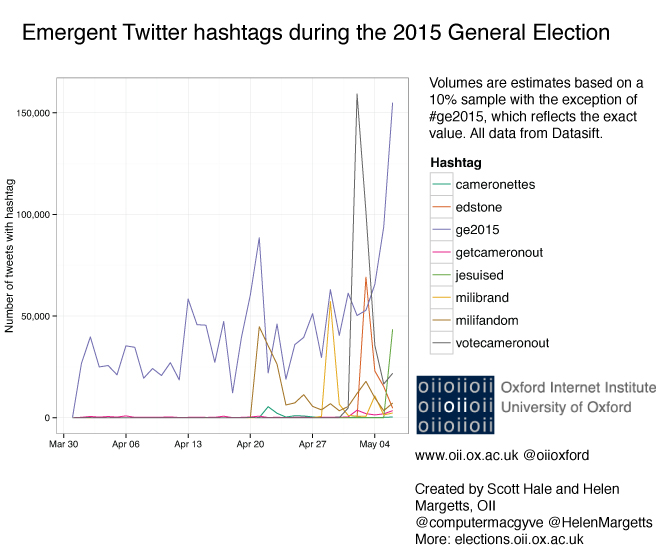
Both parties’ campaigns were tightly controlled. Ostensibly, Labour generated far more bottom-up activity from supporters using social media, through memes like #votecameron out, #milibrand (responding to Miliband’s interview with Russell Brand), and what Miliband himself termed the most unlikely cult of the 21st century in his resignation speech, #milifandom, none of which came directly from Central Office. These produced peaks of activity on Twitter that at some points exceeded even discussion of the election itself on the semi-official #GE2015 used by the parties, as the figure below shows. But the party remained aloof from these conversations, fearful of mainstream media mockery.
The Brand interview was agreed to out of desperation and can have made little difference to the vote (partly because Brand endorsed Miliband only after the deadline for voter registration: young voters suddenly overcome by an enthusiasm for participatory democracy after Brand’s public volte face on the utility of voting will have remained disenfranchised). But engaging with the swathes of young people who spend increasing amounts of their time on social media is a strategy for engagement that all parties ought to consider. YouTubers like PewDiePie have tens of millions of subscribers and billions of video views – their videos may seem unbelievably silly to many, but it is here that a good chunk the next generation of voters are to be found.
Only one of the leaders had a presence on social media that managed anything like the personal touch and universal reach that Obama achieved in 2008 and 2012 based on sustained engagement with social media—Nicola Sturgeon. The SNP’s use of social media, developed in last September’s referendum on Scottish independence had spawned a whole army of digital activists. All SNP candidates started the campaign with a Twitter account. When we look at the 650 local campaigns waged across the country, by far the most productive in the sense of generating mentions was the SNP; 100 tweets from SNP local candidates generating 10 times more mentions (1,000) than 100 tweets from (for example) the Liberal Democrats.
Scottish Labour’s failure to engage with Scottish peoples in this kind of way illustrates how difficult it is to suddenly develop relationships on social media—followers on all platforms are built up over years, not in the short space of a campaign. In strong contrast, advertising on these platforms as the Conservatives did is instantaneous, and based on the data science understanding (through advertising algorithms) of the platform itself. It doesn’t require huge databases of supporters—it doesn’t build up relationships between the party and supporters—indeed, they may remain anonymous to the party. It’s quick, dirty and effective.
The pollsters’ terrible night
So neither of the two largest parties really did anything with social media, or the huge databases of interactions that their platforms will have generated, to generate long-running engagement with the electorate. The campaigns were disconnected from their supporters, from their grass roots.
But the differing use of social media by the parties could lend a clue to why the opinion polls throughout the campaign got it so wrong, underestimating the Conservative lead by an average of five per cent. The social media data that may be gathered from this or any campaign is a valuable source of information about what the parties are doing, how they are being received, and what people are thinking or talking about in this important space—where so many people spend so much of their time. Of course, it is difficult to read from the outside; Andrew Cooper labeled the Conservatives’ campaign of big data to identify undecided voters, and micro-targeting on social media, as ‘silent and invisible’ and it seems to have been so to the polls.
Many voters were undecided until the last minute, or decided not to vote, which is impossible to predict with polls (bar the exit poll)—but possibly observable on social media, such as the spikes in attention to UKIP on Wikipedia towards the end of the campaign, which may have signalled their impressive share of the vote. As Jim Messina put it to msnbc news following up on his May 8th tweet that UK (and US) polling was ‘completely broken’—‘people communicate in different ways now’, arguing that the Miliband campaign had tried to go back to the 1970s.
Surveys—such as polls—give a (hopefully) representative picture of what people think they might do. Social media data provide an (unrepresentative) picture of what people really said or did. Long-running opinion surveys (such as the Ipsos MORI Issues Index) can monitor the hopes and fears of the electorate in between elections, but attention tends to focus on the huge barrage of opinion polls at election time—which are geared entirely at predicting the election result, and which do not contribute to more general understanding of voters. In contrast, social media are a good way to track rapid bursts in mobilisation or support, which reflect immediately on social media platforms—and could also be developed to illustrate more long running trends, such as unpopular policies or failing services.
As opinion surveys face more and more challenges, there is surely good reason to supplement them with social media data, which reflect what people are really thinking on an ongoing basis—like, a video in rather than the irregular snapshots taken by polls. As a leading pollster João Francisco Meira, director of Vox Populi in Brazil (which is doing innovative work in using social media data to understand public opinion) put it in conversation with one of the authors in April – ‘we have spent so long trying to hear what people are saying—now they are crying out to be heard, every day’. It is a question of pollsters working out how to listen.
Political big data
Analysts of political behaviour—academics as well as pollsters—need to pay attention to this data. At the OII we gathered large quantities of data from Facebook, Twitter, Wikipedia and YouTube in the lead-up to the election campaign, including mentions of all candidates (as did Demos’s Centre for the Analysis of Social Media). Using this data we will be able, for example, to work out the relationship between local social media campaigns and the parties’ share of the vote, as well as modeling the relationship between social media presence and turnout.
We can already see that the story of the local campaigns varied enormously—while at the start of the campaign some candidates were probably requesting new passwords for their rusty Twitter accounts, some already had an ongoing relationship with their constituents (or potential constituents), which they could build on during the campaign. One of the candidates to take over the Labour party leadership, Chuka Umunna, joined Twitter in April 2009 and now has 100K followers, which will be useful in the forthcoming leadership contest.
Election results inject data into a research field that lacks ‘big data’. Data hungry political scientists will analyse these data in every way imaginable for the next five years. But data in between elections, for example relating to democratic or civic engagement or political mobilization, has traditionally been woefully short in our discipline. Analysis of the social media campaigns in #GE2015 will start to provide a foundation to understand patterns and trends in voting behaviour, particularly when linked to other sources of data, such as the actual constituency-level voting results and even discredited polls—which may yet yield insight, even having failed to achieve their predictive aims. As the OII’s Jonathan Bright and Taha Yasseri have argued, we need ‘a theory-informed model to drive social media predictions, that is based on an understanding of how the data is generated and hence enables us to correct for certain biases’
A political data science
Parties, pollsters and political analysts should all be thinking about these digital disconnects in #GE2015, rather than burying them with their hopes for this election. As I argued in a previous post, let’s use data generated by social media to understand political behaviour and institutions on an ongoing basis. Let’s find a way of incorporating social media analysis into polling models, for example by linking survey datasets to big data of this kind. The more such activity moves beyond the election campaign itself, the more useful social media data will be in tracking the underlying trends and patterns in political behaviour.
And for the parties, these kind of ways of understanding and interacting with voters needs to be institutionalised in party structures, from top to bottom. On 8th May, the VP of a policy think-tank tweeted to both Axelrod and Messina ‘Gentlemen, welcome back to America. Let’s win the next one on this side of the pond’. The UK parties are on their own now. We must hope they use the time to build an ongoing dialogue with citizens and voters, learning from the success of the new online interest group barons, such as 38 degrees and Avaaz, by treating all internet contacts as ‘members’ and interacting with them on a regular basis. Don’t wait until 2020!
Helen Margetts is the Director of the OII, and Professor of Society and the Internet. She is a political scientist specialising in digital era governance and politics, investigating political behaviour, digital government and government-citizen interactions in the age of the internet, social media and big data. She has published over a hundred books, articles and major research reports in this area, including Political Turbulence: How Social Media Shape Collective Action (with Peter John, Scott Hale and Taha Yasseri, 2015).
Scott A. Hale is a Data Scientist at the OII. He develops and applies techniques from computer science to research questions in the social sciences. He is particularly interested in the area of human-computer interaction and the spread of information between speakers of different languages online and the roles of bilingual Internet users. He is also interested in collective action and politics more generally.