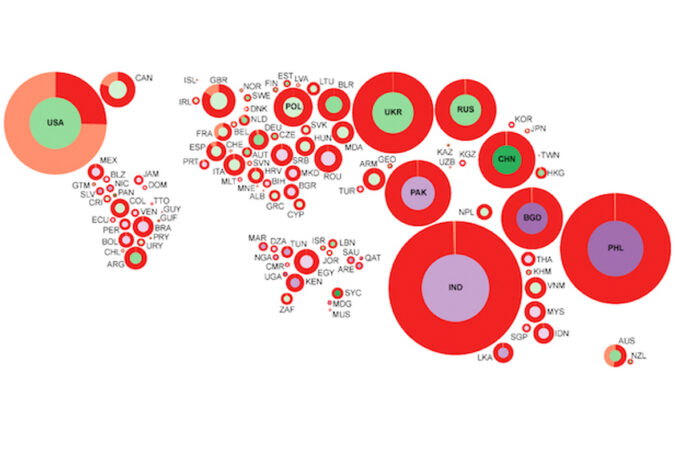
The cartogram depicts countries as circles sized according to dollar inflow during March 2013 on a major online labour platform. The shading of the inner circle indicates the median hourly rate published by digital workers in that country. See the report for details.
The growth of online gig work—paid work allocated and delivered by way of internet platforms without a contract for long-term employment—has been welcomed by economic development experts, and the world’s largest global development network is promoting its potential to aid human development. There are hopes that online gig work, and the platforms that support it, might catalyse new, sustainable employment opportunities by addressing a mismatch in the supply and demand of labour globally. Some of the world’s largest gig work platforms have also framed their business models as a revolution in labour markets, suggesting that they can help lift people out of poverty. Similarly, many policymakers expect that regions like Sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia can capitalise on this digitally mediated work opportunity as youth-to-adult unemployment rates hit historic peaks. More broadly, it has been suggested that online gig work will have structural benefits on the global economy, such as raising labour force participation and improving productivity. Against this background, a new report by Mark Graham, Vili Lehdonvirta, Alex Wood, Helena Barnard, Isis Hjorth, and David Peter Simon, “The Risks and Rewards of Online Gig Work At The Global Margins” [PDF] highlights the risks alongside the rewards of online gig work. It draws on interviews and surveys, together with transaction data from one of the world’s largest online gig work platforms, to reveal the complex and sometimes problematic reality of this “new world of work”. While there are significant rewards to online gig work, there are also significant risks. Discrimination, low pay rates, overwork, and insecurity all need to be tackled head-on. The report encourages online gig work platforms to further develop their service, policymakers to revisit regulation, and labour activists to examine organising tactics if online gig work is to truly live up to its potential for human development, and become a sustainable situation for many more workers. The final section of the report poses questions for all stakeholders…

